Using EdgeDB AI
EdgeDB AI allows you to ship AI-enabled apps with practically no effort. It automatically generates embeddings for your data. Works with OpenAI, Mistral AI, Anthropic, and any other provider with a compatible API.
Enable extension in your schema
AI is an EdgeDB extension. To enable it, you will need to add the extension to your app’s schema:
using extension ai;Extension configuration
The AI extension may be configured via our UI or via EdgeQL. To use the
built-in UI, access it by running edgedb ui. If you have the extension
enabled in your schema as shown above and have migrated that schema change, you
will see the “AI Admin” icon in the left-hand toolbar.
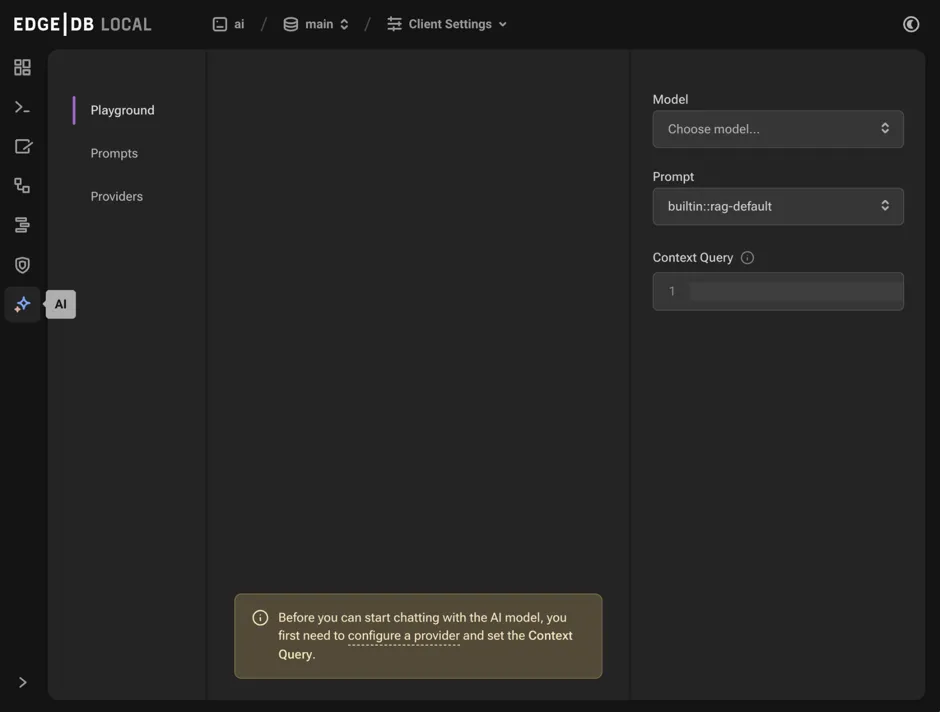
The default tab “Playground” allows you to test queries against your data after you first configure the model, prompt, and context query in the right sidebar.
The “Prompts” tab allows you to configure prompts for use in the playground. The “Providers” tab must be configured for the API you want to use for embedding generation and querying. We currently support OpenAI, Mistral AI, and Anthropic.
Configuring a provider
To configure a provider, you will first need to obtain an API key for your chosen provider, which you may do from their respective sites:
With your API key, you may now configure in the UI by clickin the “Add Provider” button, selecting the appropriate API, and pasting your key in the “Secret” field.
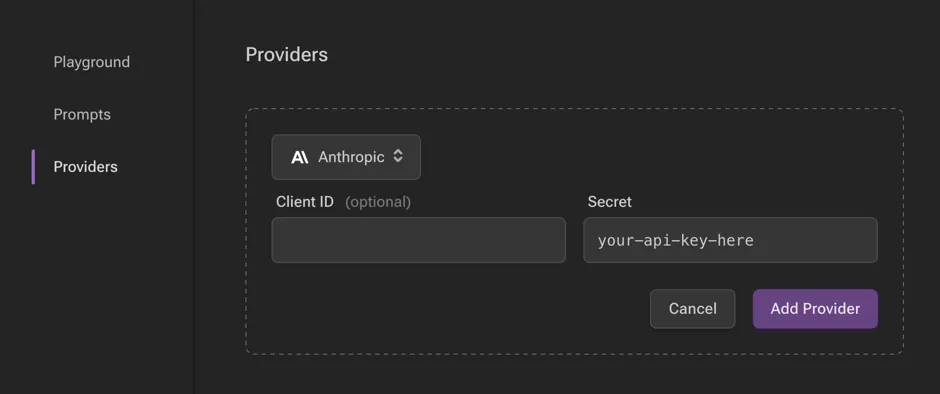
You may alternatively configure a provider via EdgeQL:
configure current database
insert ext::ai::OpenAIProviderConfig {
secret := 'sk-....',
};This object has other properties as well, including client_id and
api_url, which can be set as strings to override the defaults for the
chosen provider.
We have provider config types for each of the three supported APIs:
-
OpenAIProviderConfig -
MistralProviderConfig -
AnthropicProviderConfig
Usage
Using EdgeDB AI requires some changes to your schema.
Add an index
To start using EdgeDB AI on a type, create an index:
module default {
type Astronomy {
content: str;
deferred index ext::ai::index(embedding_model := 'text-embedding-3-small')
on (.content);
}
};In this example, we have added an AI index on the Astronomy type’s
content property using the text-embedding-3-small model. Once you have
the index in your schema, create and
apply your migration, and you’re ready
to start running queries!
The particular embedding model we’ve chosen here
(text-embedding-3-small) is an OpenAI model, so it will require an
OpenAI provider to be configured as described above.
You may use any of these pre-configured embedding generation models:
OpenAI
-
text-embedding-3-small -
text-embedding-3-large -
text-embedding-ada-002
Learn more about the OpenAI embedding models
Mistral
-
mistral-embed
You may want to include multiple properties in your AI index. Fortunately, you can define an AI index on an expression:
module default {
type Astronomy {
climate: str;
atmosphere: str;
deferred index ext::ai::index(embedding_model := 'text-embedding-3-small')
on (.climate ++ ' ' ++ .atmosphere);
}
};Run a semantic similarity query
Once your index has been migrated, running a query against the embeddings is super simple:
select ext::ai::search(Astronomy, query)Simple, but you’ll still need to generate embeddings from your query or pass in existing embeddings. If your ultimate goal is retrieval-augmented generation (i.e., RAG), we’ve got you covered.
Use RAG via HTTP
By making an HTTP request to
https://<edgedb-host>:<port>/branch/<branch-name>/ai/rag, you can generate
text via the generative AI API of your choice within the context of a type with
a deferred embedding index.
Making HTTP requests to EdgeDB requires authentication.
$
curl --json '{ "query": "What color is the sky on Mars?",
"model": "gpt-4-turbo-preview",
"context": {"query":"select Astronomy"}
}' https://<edgedb-host>:<port>/branch/<branch-name>/ai/rag
{"response": "The sky on Mars is red."}Since LLMs are often slow, it may be useful to stream the response. To do this,
add "stream": true to your request JSON.
The particular text generation model we’ve chosen here
(gpt-4-turbo-preview) is an OpenAI model, so it will require an OpenAI
provider to be configured as described above.
You may use any of these text generation models:
OpenAI
-
gpt-3.5-turbo -
gpt-4-turbo-preview
Learn more about the OpenAI text generation models
Mistral
-
mistral-small-latest -
mistral-medium-latest -
mistral-large-latest
Learn more about the Mistral text generation models
Anthropic
-
claude-3-haiku-20240307 -
claude-3-sonnet-20240229 -
claude-3-opus-20240229
Use RAG via JavaScript
@edgedb/ai offers a convenient wrapper around ext::ai. Install it with
npm install @edgedb/ai (or via your package manager of choice) and
implement it like this example:
import { createClient } from "edgedb";
import { createAI } from "@edgedb/ai";
const client = createClient();
const gpt4AI = createAI(client, {
model: "gpt-4-turbo-preview",
});
const blogAI = gpt4AI.withContext({
query: "select Astronomy"
});
console.log(await blogAI.queryRag(
"What color is the sky on Mars?"
));